This surgery is performed as a
day care operation where the patient can go home the same
evening and has no stitches in his legs.
| | Trendelenberg
position with 20 - 30° head down |
|
|
Legs abducted 10 -15° |
| |
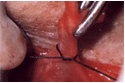
Saphenofemoral junction (SFJ) found 2 cm below and lateral to pubic tubercle |
| | Essential
to identify SFJ before performing flush ligation of the LSV |
|
|
Individually divide and ligate all tributaries of the LSV |
| |
| Superficial
circumflex iliac vein | | | Superficial
inferior epigastric vein | | | Superficial
and deep external pudendal vein | |
|
| Check
that femoral vein clear of direct branches for 1 cm above and below SFJ |
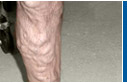
| | Stripping
of LSV reduces risk of recurrence |
|
| Only
strip to upper calf. |
| |
Stripping to ankle is associated with increased risk of saphenous neuralgia |
| | Post
operative care: |
| | | Elevate
foot of bed for 12 hours | | | Class
2 stockings
should be worn for at least 2 weeks | |